- Amman, King Hussain Park, Jordan
- +(962) 000-0000
- info@curafile.com
Blood Clots in The Lung
- Home
- Lungs and Breathing
- Blood Clots in The Lung
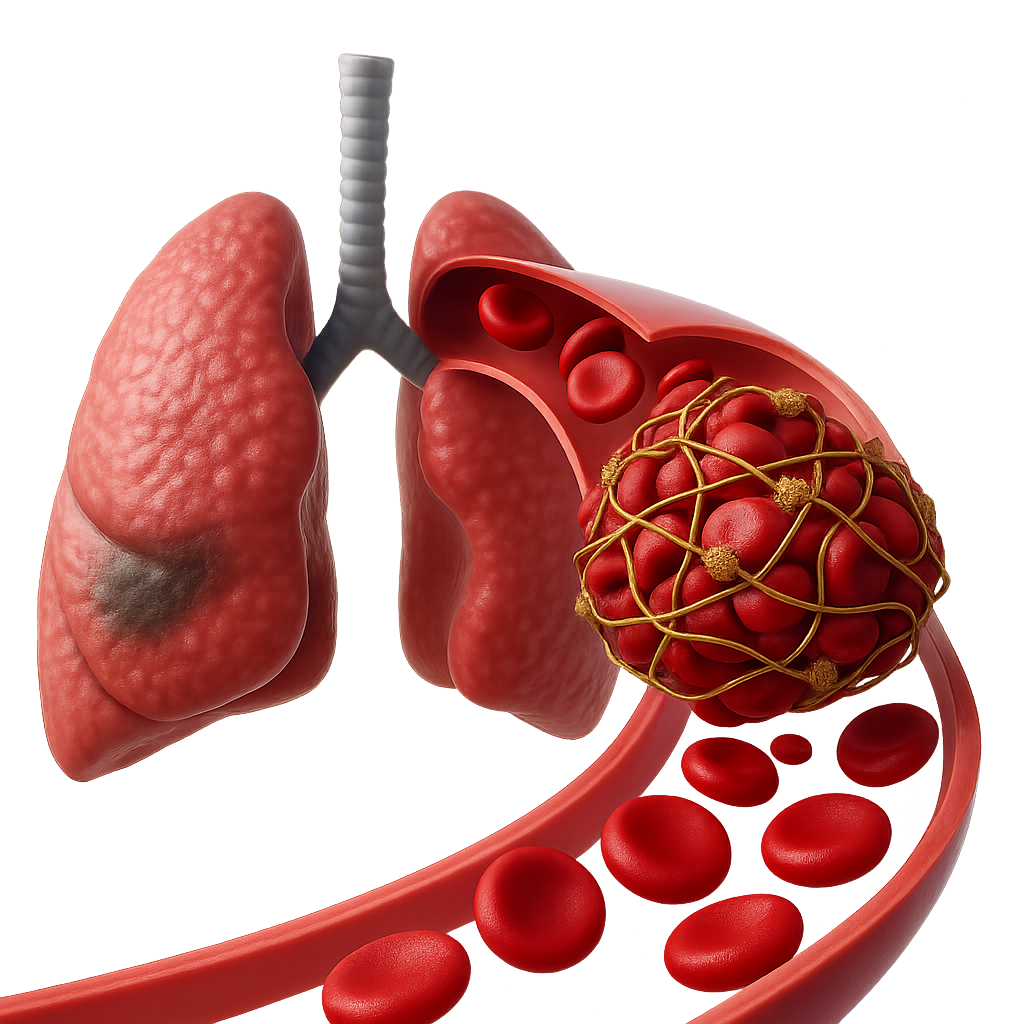
A pulmonary embolism (PE) is a sudden blockage in a lung artery. It usually happens when a blood clot breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream to the lungs. PE is a serious condition that can cause:
- Permanent damage to the lungs
- Low oxygen levels in your blood
- Damage to other organs in your body from not getting enough oxygen
PE can be life-threatening, especially if a clot is large, or if there are many clots.
Symptoms of PE include:
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid breathing
- Chest pain or discomfort, which usually gets worse when you cough or take a deep breath
- Increased heart rate
- Coughing up blood
- Very low blood pressure, lightheadedness, or fainting
Sometimes people with PE don’t have any symptoms until they have serious complications, such as pulmonary hypertension (high blood pressure in the arteries to your lungs).
The cause is usually a blood clot that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream to the lungs. The clot is usually a deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a clot in the leg. In rare cases, material such as air bubbles, clumps of fat, or parts of a tumor can block the lung artery and cause PE
If you have PE, you need medical treatment right away. The goal of treatment is to break up clots and help keep other clots from forming. Treatment options include medicines and procedures.
Medicines:
- Anticoagulants, or blood thinners, keep blood clots from getting larger and stop new clots from forming. You might get them as an injection, a pill, or through an I.V. (intravenous). They can cause bleeding, especially if you are taking other medicines that also thin your blood, such as aspirin.
- Thrombolytics are medicines to dissolve blood clots. You may get them if you have large clots that cause severe symptoms or other serious complications. Thrombolytics can cause sudden bleeding, so they are used if your PE is serious and may be life-threatening.
Procedures:
- Catheter-assisted thrombus removal uses a flexible tube to reach a blood clot in your lung. Your health care provider can insert a tool in the tube to break up the clot or to deliver medicine through the tube. Usually you will get medicine to put you to sleep for this procedure.
- A vena cava filter may be used in some people who cannot take blood thinners. Your health care provider inserts a filter inside a large vein called the vena cava. The filter catches blood clots before they travel to the lungs, which prevents pulmonary embolism. But the filter does not stop new blood clots from forming.
Can pulmonary embolism (PE) be prevented?
Preventing new blood clots can prevent PE. Prevention may include:
- Continuing to take blood thinners. It’s also important to get regular checkups with your provider, to make sure that the dosage of your medicines is working to prevent blood clots but not causing bleeding.
- Heart-healthy lifestyle changes, such as heart-healthy eating, exercise, and, if you smoke, quitting smoking. Using compression stockings to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- Moving your legs when sitting for long periods of time (such as on long trips).
- Moving around as soon as possible after surgery or being confined to a bed.
Who is more likely to develop a pulmonary embolism (PE)?
Anyone can get a pulmonary embolism (PE), but certain things can raise your risk of PE:
- Having surgery, especially joint replacement surgery.
- Certain medical conditions, including
- Cancers
- Heart diseases
- Lung diseases
- A broken hip or leg bone or other trauma
- Hormone-based medicines, such as birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy.
- Pregnancy and childbirth. The risk is highest for about six weeks after childbirth.
- Not moving for long periods, such as being on bed rest, having a cast, or taking a long plane flight.
- Age. Your risk increases as you get older, especially after age 40.
- Family history and genetics. Certain genetic changes that can increase your risk of blood clots and PE.
- Obesity.
How is a pulmonary embolism (PE) diagnosed?
It can be difficult to diagnose PE. To find out if you have a PE, your health care provider will:
- Take your medical history, including asking about your symptoms and risk factors for PE
- Do a physical exam
- Likely order some tests, including various imaging and blood tests
Can pulmonary embolism (PE) be prevented?
Preventing new blood clots can prevent PE. Prevention may include:
- Continuing to take blood thinners. It’s also important to get regular checkups with your provider, to make sure that the dosage of your medicines is working to prevent blood clots but not causing bleeding.
- Heart-healthy lifestyle changes, such as heart-healthy eating, exercise, and, if you smoke, quitting smoking. Using compression stockings to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- Moving your legs when sitting for long periods of time (such as on long trips).
- Moving around as soon as possible after surgery or being confined to a bed.
Related Topics
Good Habits You Should Know
Bad Habits You Should Know
-
Find a clinic near you
-
Call for an appointment!
-
Feel free to message us!
About Us
Curafile is the biggest Healthcare Curated Network Globally that serves citizens, service providers in B2C and B2B directions.
- Al Hussain Business Park
Amman, Jordan
Additional Links
- test October 20, 2025
- Hello world! October 7, 2025
- Many doctors use wrong test to diagnose kids food allergies February 12, 2017
- Rising cost of diabetes care concerns patients and doctors January 15, 2017
- Can breakfast help keep us thin? Nutrition science is tricky January 5, 2017
