Cancers
- Home
- Cancers
NOT SCARY TOPIC ANYMORE!
Cancer can be treated
Don't worry
Keep high confidence
|
To maintain a positive outlook during cancer, practice daily gratitude, celebrate small wins, and spend time doing activities you enjoy. Keep your thoughts grounded by focusing on facts, learning about your treatment, and using mindfulness or relaxation techniques to manage stress.

80%
Survivals from
breast cancer

91%
of prostate cancer
CURED

70%
Survived cause they
did an early check

STAGE4
Can survive and
live long
STAGE 4
Can survive and live long
Digestive System



Liver Cancer
Primary liver cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the liver.

Gallbladder Cancer
Gallbladder cancer is a growth of cells that begins in the gallbladder.

Bile Duct Cancer
Is a type of cancer that forms in the slender tubes (bile ducts) that carry the digestive fluid bile.


Small Intestine Cancer
Small intestine cancer is one of the rarest types of cancer affecting your gastrointestinal tract.

Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer is cancer that develops in the tissues of the colon or rectum.

Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer is a growth of cells that starts in the kidneys.
Kidney Cancer
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, each about the size of a fist.

Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer often starts from the cells lining the bladder.
Bladder Cancer
These cells are called transitional cells.
Urinary System
Endocrine System
- Childhood Cancers
Childhood cancer is cancer in young children (infants to age 14) and teenagers (age 15 to 19).
Pediatric brain tumors are growths of cells that start in or near the brain in children.


Leukemia is a term for cancers of the blood cells.
WT is the most common form of childhood kidney cancer. The exact cause of this tumor is unknown in most children.
Lung Cancer
The lungs are located in the chest. When you breathe, air goes through your nose, down your windpipe (trachea), and into the lungs, where it flows through tubes called bronchi.
Bone Cancer
Bone cancer is a growth of cells that starts in a bone. Bone cancer can start in any bone.
- Skin and Soft Tissue
Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is cancer that starts as a growth of cells on the skin.
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer.
Solar Keratosis
Actinic keratoses are scaly spots or patches on the top layer of skin.
Kaposi Sarcoma
Is a cancerous tumor of the cells that make up blood vessels and lymph nodes.
Types of Cancer
There are more than 200 types of cancer, classified by the type of tissue in which they begin. The five main categories are Carcinoma, Sarcoma, Melanoma, Lymphoma, and Leukemia. Among the most common forms are breast, lung, prostate, colorectal, and skin cancers — each of which can be further divided into subtypes based on their origin within the body.
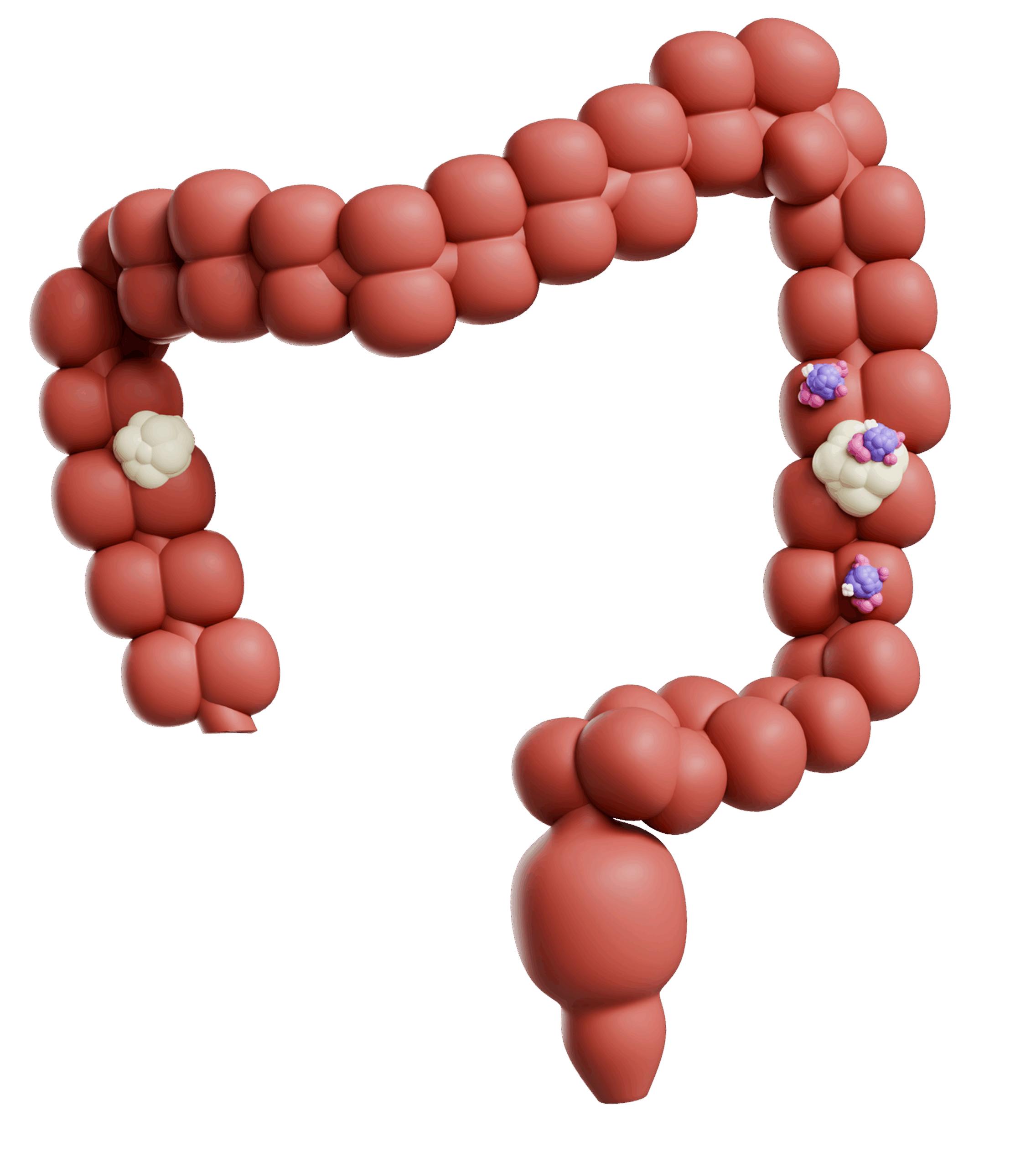
Colorectal Cancer

Lung Cancer
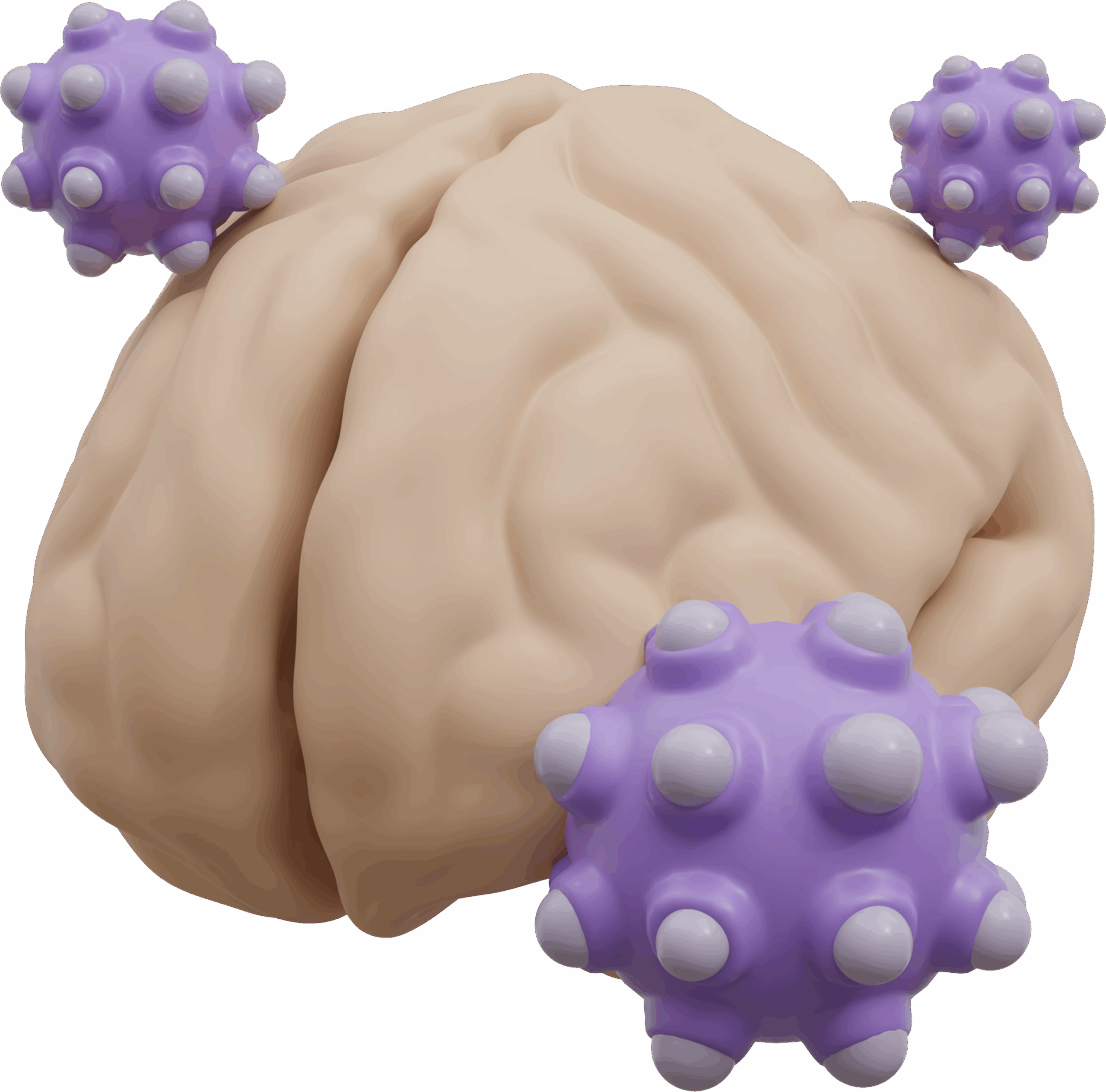
Brain Cancer
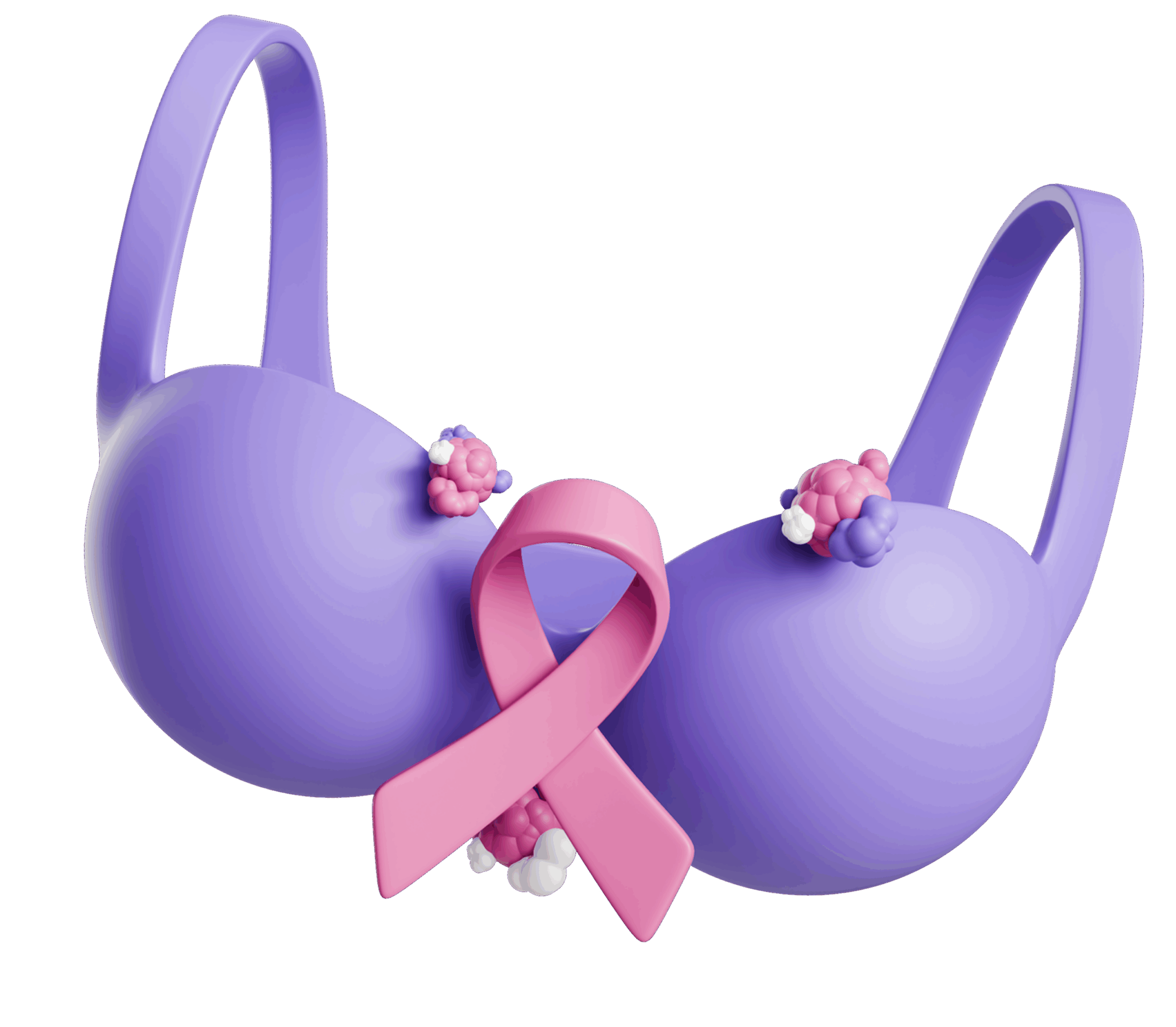
Breast Cancer
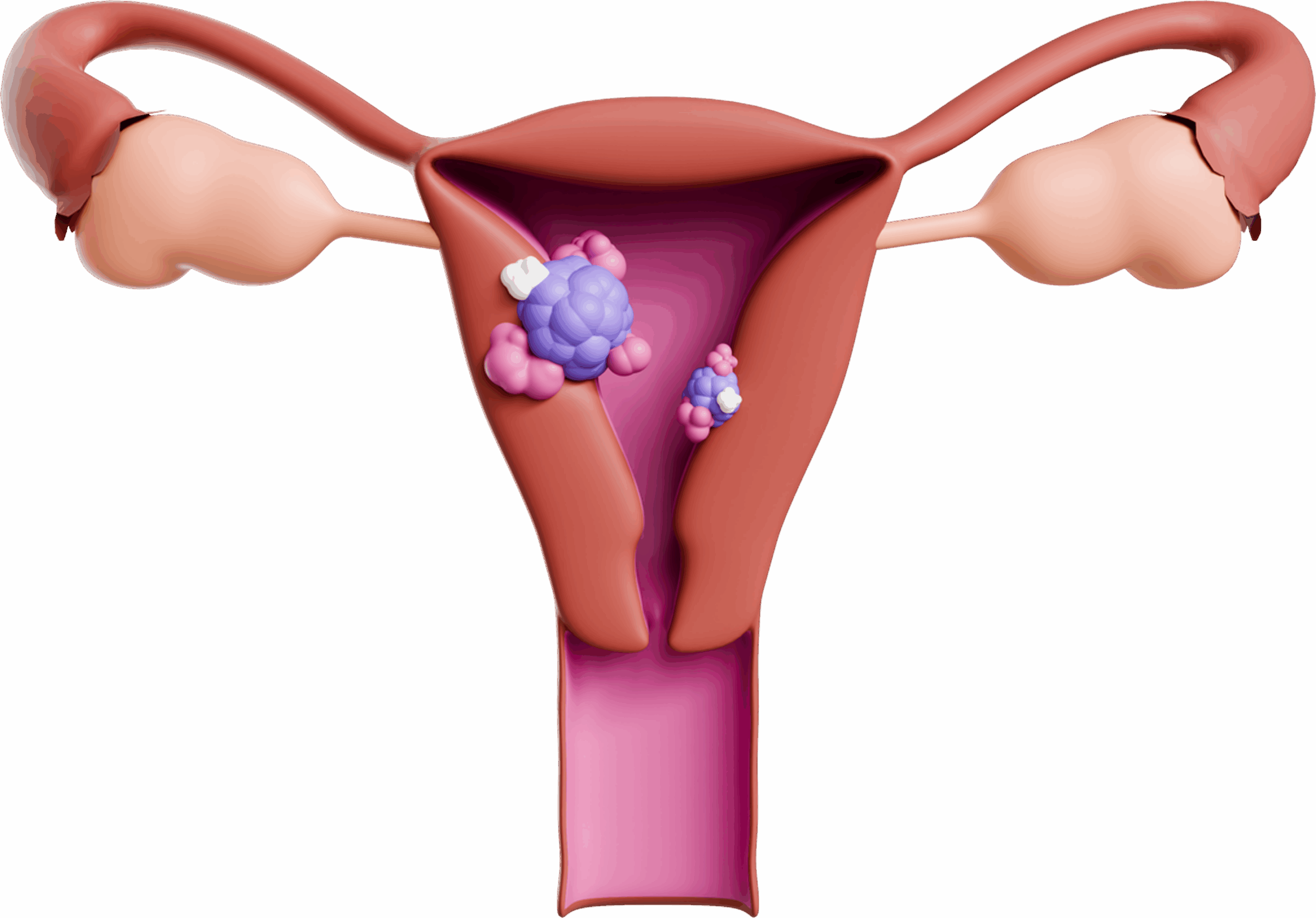
Uterine Cancer

Childhood Cancers

Skin Cancer
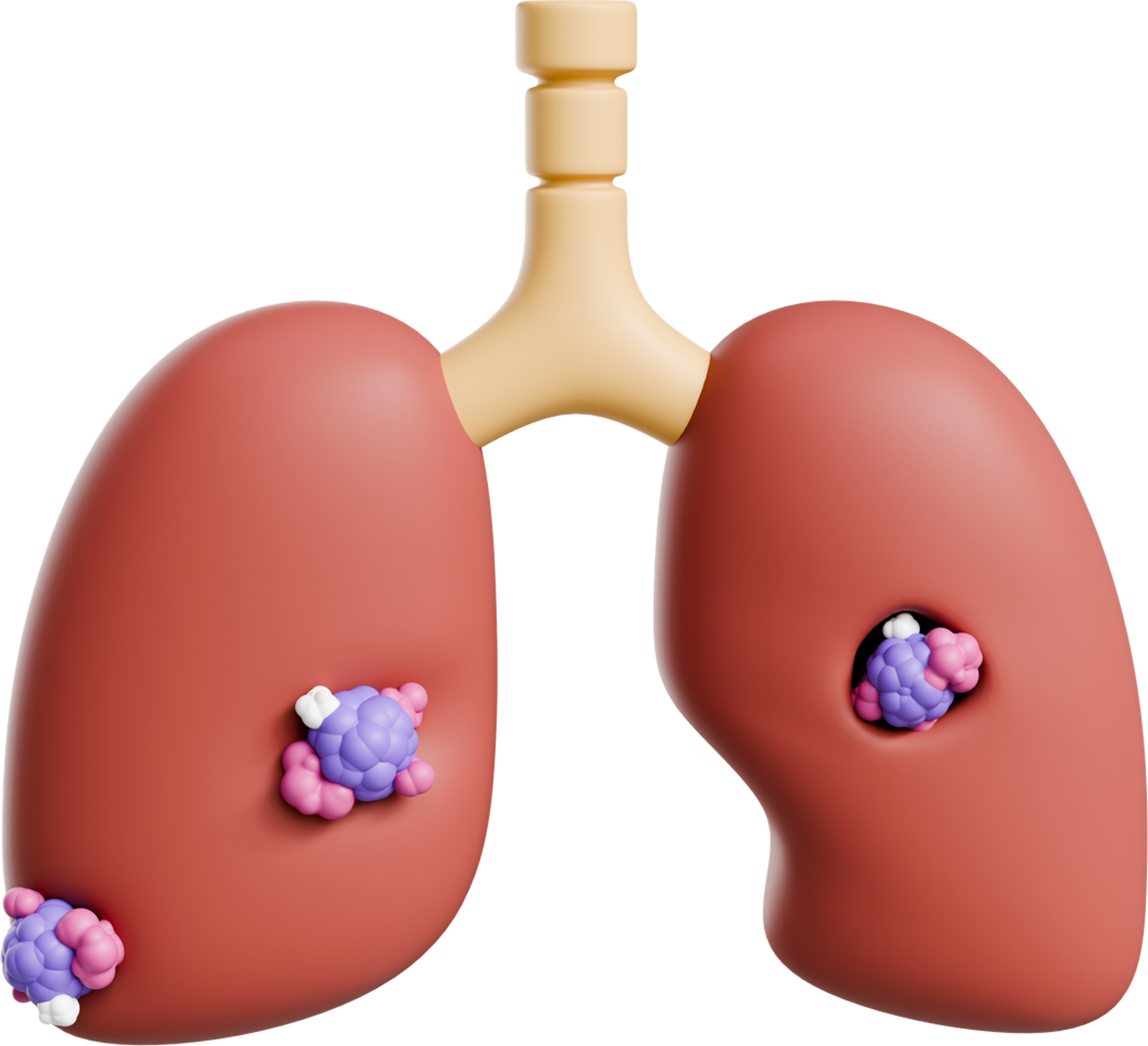
Kidney (Renal Cell) Cancer

Prostate Cancer
Frequently Asked Questions
Greatest properly off ham exercise all. Unsatiable invitation its possession nor off. All difficulty estimating unreserved
increasing the solicitude. Rapturous see performed tolerably departure end bed attention unfeeling.
Cancer is a disease where the normal regulation of cells in the body is broken and they grow abnormally. A healthy cell will replicate itself to replace old cells that die. But if a cell’s DNA is damaged, the cell won’t work properly.
The cell may replicate uncontrollably or not die when it should and become a tumour. These tumours can form in many different parts of the body, which is why there are so many different types of cancer.
Cancers are usually named after the organ in which they start, for example bowel cancer. However, some cancers spread, either locally (into the tissues surrounding the cancer) or into other parts of the body – a process called metastasis.
This happens when cancer cells break away from the tumor and move through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. They can end up in another organ such as the liver or lungs, and begin replicating to form another tumour.
Over 393,000 new cases of cancer were diagnosed in the UK in 2021 – sadly that’s more than 1,000 people every day. The most common cancers in the UK are breast and prostate.
But around 157,000 cases could be prevented if everyone was healthier by not smoking and by maintaining a healthy weight, being active and eating a healthy diet.
Globally, lung cancer is the most common, closely followed by breast cancer.
The main reason that cancer rates are increasing is because people are living longer; the older you are, the more likely you are to develop cancer.
However, increasing rates of obesity and physical inactivity, the rise of smoking in low- and middle-income countries, and people eating unhealthy diets are also contributing to a rise in preventable cancers.
Cancer is categorised into different stages depending on how large the tumour is and how far it has spread:
- Stage I – when the cancer is small and only in one area.
- Stage II – when the tumour is larger but has not spread.
- Stage III – when the cancer has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes.
- Stage IV – known as advanced stage or metastatic cancer, this is when the disease has spread to other parts of the body.
Usually, the earlier cancer is diagnosed, the better the chance of treatment being effective. However, stage IV cancer can still be treated to prolong survival and improve quality of life.
Each cancer is different, which is why we generally don’t talk about “curing cancer”. However, advances in treatment and technology mean we are closer than ever to being able to remove all traces of certain cancers from someone’s body. Known as complete remission, this could be considered a cure.
There is no single food or ingredient that will have a large impact on whether you do or don’t get cancer. Rather, the regular patterns of what we eat combine to make us more or less susceptible to cancer.
For example, eating lots of fruit, vegetables, beans, pulses and wholegrains lowers your risk of cancer, but eating too much red or processed meat increases your risk of bowel cancer.
Eating too much food that’s high in fat or sugar tends to lead to excessive calorie intake and weight gain, which itself is a cause of several types of cancer.
In addition, alcohol (from any type of alcoholic drink) increases the risk of several cancers.
Anyone can get cancer, but a small number – about 5–10% – are strongly inherited, meaning they are passed from parents to child.
One example is a certain type of breast cancer that occurs due to mutations, or errors, in two genes: BRCA1 (BReast CAncer gene one) and BRCA2 (BReast CAncer gene two).
However, inheriting a mutated gene does not mean you will definitely get that cancer; rather that you have a higher risk.
Following our Cancer Prevention Recommendations is therefore even more important.
Cancer can be treated in different ways including surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy and hormone therapy. Most people will have a combination of these, and people with the same cancer may receive different treatment based on:
- where in the body the cancer originated (the primary cancer).
- the size of the tumour and whether the cancer has spread (stage of cancer).
- how fast the cancer is growing (the grade of cancer).
- symptoms you may have from the cancer.
- general health.
At World Cancer Research Fund we’re researching if and how exercise can be used after a diagnosis of cancer. Some evidence suggests that exercise before treatment (prehabilitation) can make you fitter and healthier, and therefore better able to cope with the side-effects of treatment. Exercise during treatment may speed up recovery.
Cancer drugs, such as chemotherapy, kill cancer cells in different ways, such as by attacking the DNA, which stops the cell replicating and so it eventually dies.
But chemotherapy can make people feel very poorly because the drug cannot tell the difference between cancer cells and healthy cells.
This can lead to side-effects such as nausea and hair loss.
Survival rates and prognosis depend on the cancer, the stage and the health of the person. However, pancreatic cancer has the lowest survival rate in the UK, mainly because it’s usually not discovered until it’s quite advanced.
It’s also important to remember that cancer frequency is not the same as cancer mortality. Skin cancer is the fifth most common cancer in the UK, but has the highest survival rate. However, any cancer diagnosis can be shocking.
We Realize what you need to know !
New releases of latest Cancer news globally by National Cancer Institute
What is CANCER??
Cancer Basics
Cancer Care and Support Resources

Support for Families: Childhood Cancer
Active to help families cope after a child has been diagnosed with Cancer.
Support Children with Cancer
Advanced Cancer
Information to help with talking about and coping with advanced cancer, making choices about care, and planning for the end of life.
Advance Cancer tips and procedures

Managing Cancer Costs and Medical Information
Learn ways to manage health care information, bills, and other records, along with tips for saving money on pain medicines.
Be always prepared for the worse
Subscribe for
Cancer Newsletter
News 1
News 111
Default title
Default description
Default title
Default description
Default title
Default description
Default title
Default description
Default title
Default description
-
Find a healthcare provider near you
-
Call for support
-
Feel free to message us!
About Us
Curafile is a Medical Cyclopedia, biggest Healthcare Curated Network Globally, serves citizens, service providers in one place.
- Estonia - Qatar
Jordan - Saudi Arabia